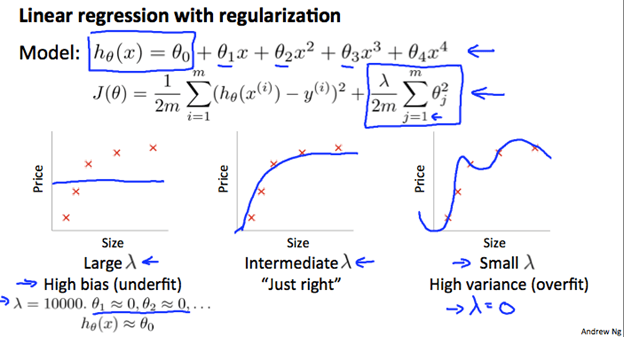
We can also see that changing the regularization parameter also helps. A list of lambda’s should be created and a learning model should go through each lambda, learn new theta, and then find the training test error + cross set validation error. The lambda which produces the output with the least cost should be used.
Let us look at two final graphs to understand how to diagnose high variance/high bias. As you add features too a learning model, the greater the error becomes because more data points will not be exactly on the line of best fit. So plotting the error as a function of training set size would be beneficial to see. The name for these graphs are called learning curves.
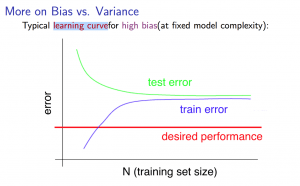
This learning curve has a very high-test error and a very high train error, which is above the desired performance. What do you think this is high variance or high bias? Does it overfit or underfit? For the training error to be high and similar to the test error, it is likely that the learning model underfit the data, therefore causing high bias.
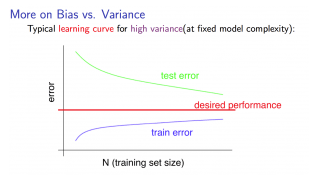
Let’s look at another graph. This one has a train error lower than what our goal is, but the test error is still higher than what we want. The values are far apart which suggests high variance, therefore, overfitting.